KakkoKari (仮) Another (data) science blog. By Alessandro Morita
Attention: a tale of three spaces
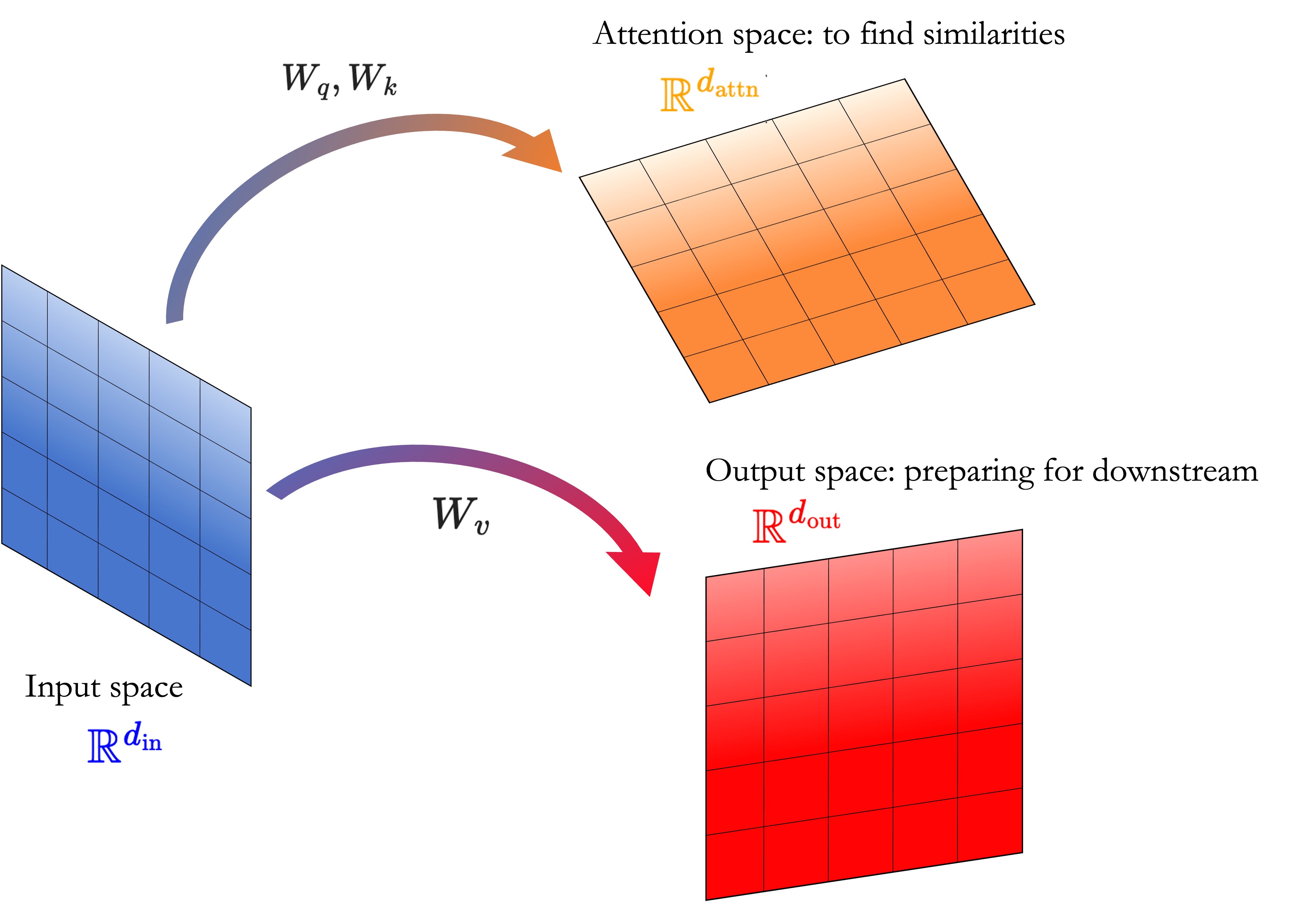
I admit I always had some trouble understanding Attention in the context of Transformers. There are several good references for this - Jay Alammar’s The Illustrated Transformer is a common example. Still, I always had some difficulties building a mental model of what the attention mechanism does. Some references explain very thoroughly how to m... Read more 18 Dec 2023 - 15 minute read
13.8 billion years on a 10.1'' screen
Some moments in one’s life can be awe-inspiring. You know, those moments when you feel deeply connected to something; when things make sense. Some people would label this feeling as spiritual; not being a very spiritual person myself (at least according to the common definition), I don’t really know how appropriate this attribution is, but I ca... Read more 04 Aug 2023 - 9 minute read
Lie derivatives and cluttered notation
I’ve always had a love-hate relationship with notation in mathematics. On the one hand, I am an intuitive person who needs to understand the big picture of something before jumping into the details. In this sense, I prefer my math to be uncluttered and focusing on the key steps of a derivation. On the other hand, I also need my understanding ... Read more 25 Jun 2023 - 11 minute read
How Cartesian can we make coordinates on Earth?
Earth is locally flat. This is true not only for the (surface of) the Earth, but for any so-called Riemannian manifold, a generalization of surfaces to any number of dimensions. Even though there is curvature, if one zooms enough into a point, curvature disappears and their neighborhood will look flat. This is why some individuals in our planet... Read more 11 May 2023 - 27 minute read
My favorite math problem
Back in the second year of high school, a friend shared with me a problem that his geometry teacher had shown him. I was going through a small crisis regarding my future career. I couldn’t decide whether I wanted to pursue a major in the Humanities (Arts or Design were on the top of the list) or in STEM. Before eventually settling down on Physi... Read more 16 Apr 2023 - 4 minute read